Publications
publications by categories in reversed chronological order. generated by jekyll-scholar.
2025
- TACO
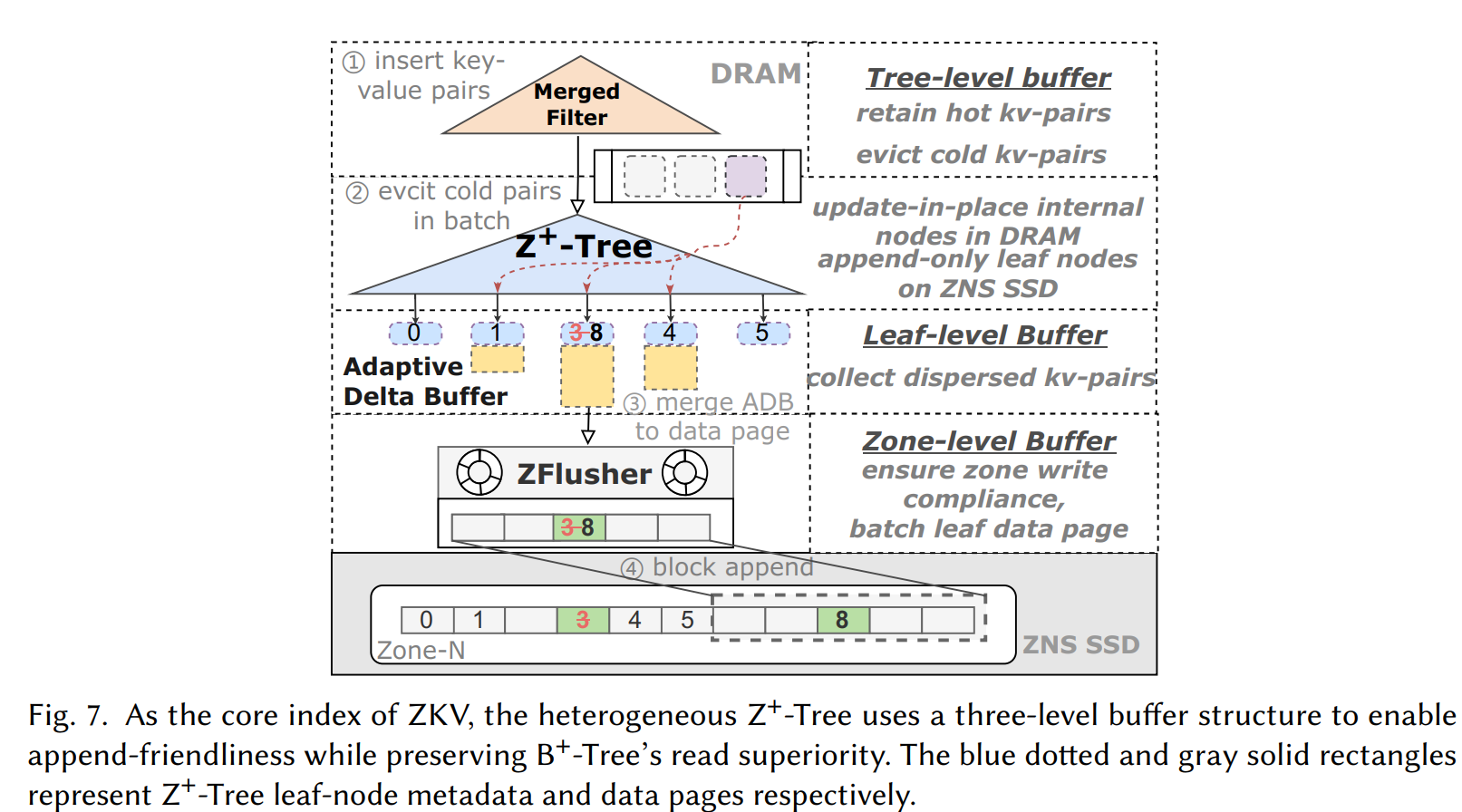 Co-design of B+-Tree Index with Emerging Zone Interfaces for Small-sized Key-Value PairsACM Transactions on Architecture and Code Optimization, 2025
Co-design of B+-Tree Index with Emerging Zone Interfaces for Small-sized Key-Value PairsACM Transactions on Architecture and Code Optimization, 2025The host-side and append-only zone interface offers new opportunities for existing key-value stores (KVSs), especially in reducing the flash-layer write amplification. While existing works focused on leveraging the zone interface for LSM-Tree-based KVSs, the potential advantages for B+-Tree-based KVSs remain under-explored. Through in-depth experimental observations, we identify three key opportunities for B+-Tree-based KVSs: superior read performance, flash-friendly append operations, and the ability to directly manage flash media.However, existing B+-Tree-based KVSs designed for block SSDs rely on inefficient file system layers to adapt to the idiosyncratic zone interface, and achieve reduced write amplification by seriously sacrificing read performance. We proposed a write-optimized B+-Tree-based key-value store ZKV, designed to minimize write amplification through the zone interface without sacrificing read performance. ZKV employs a three-level buffer structure to enable its core index structure Z+-Tree to be zone-interface efficient, including a tree-level merged filter, a leaf-level adaptive delta buffer, and an efficient zone-level management module ZFlusher.Through the three-level buffer structure, Z+-Tree effectively leverages the zone interface by converting smallsize random write operations into flash-friendly large-block append operations. Our evaluations on a real ZNS SSD device demonstrate that ZKV achieves up to 3.12x/2.53x higher insert/read throughput than the current buffered-B+-Tree-based KVSs under YCSB workloads. Under three additional real-world workloads, ZKV matches the write performance of LSM-Tree-based RocksDB while delivering the read performance of B+-Tree-based WiredTiger.
@article{Hu_2025_ZKV, title = {Co-design of B+-Tree Index with Emerging Zone Interfaces for Small-sized Key-Value Pairs}, journal = {ACM Transactions on Architecture and Code Optimization}, publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery (ACM)}, author = {}, year = {2025}, } - ICCD
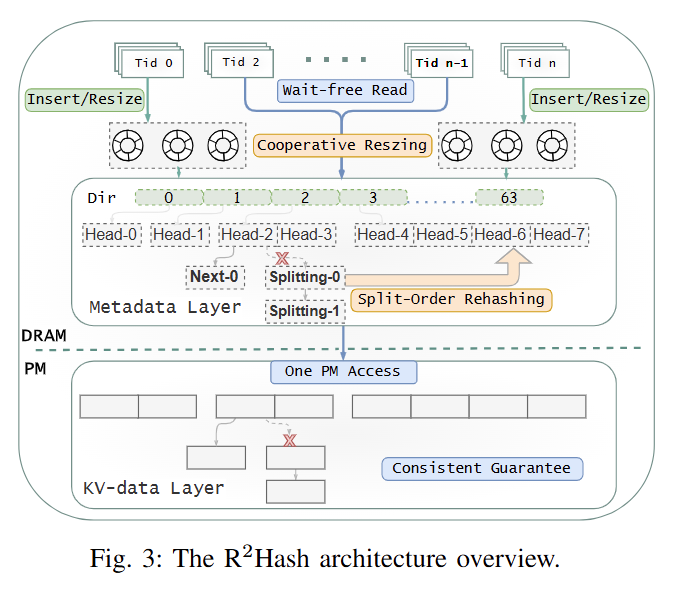 R2Hash: A Read-Optimized and Resize-Friendly Hashing Index for Persistent MemoryIn 2025 IEEE 43rd International Conference on Computer Design (ICCD), Nov 2025
R2Hash: A Read-Optimized and Resize-Friendly Hashing Index for Persistent MemoryIn 2025 IEEE 43rd International Conference on Computer Design (ICCD), Nov 2025Selected as one of the Best Paper Candidates in ICCD 2025.
Persistent memory (PM) offers a compelling combination of durability and near-DRAM performance, but it also introduces new challenges for hashing indexes. Existing persistent hashing designs prioritize resizing efficiency at the expense of increased query latency, losing the key advantage of hash tables. This paper introduces R2Hash, a persistent hash index redesigned from the persistent cache-line hash table, to balance high read performance with efficient resizing. R2Hash is guided by a migration rule, enabling it to meet both goals through two main contributions: (i) a cooperative and lowoverhead resizing strategy based on split-order hashing, and (ii) a shift-aware search combined with a two-layer bucket layout that enables lock-free reads with only one PM access on average. Furthermore, R2Hash provides log-free consistency and a nonblocking recovery mechanism. Experimental results demonstrate that R2Hash achieves up to 8.1× higher search throughput and 7.5× higher insert throughput compared to other persistent hash indexes across a range of workloads
@inproceedings{Hu_2025_RRHASH, title = {R2Hash: A Read-Optimized and Resize-Friendly Hashing Index for Persistent Memory}, booktitle = {2025 IEEE 43rd International Conference on Computer Design (ICCD)}, author = {}, year = {2025}, publisher = {IEEE Computer Society}, address = {Dallas,Texas,USA}, month = nov, } - TACOZNSFQ: An Efficient and High-Performance Fair Queue Scheduling Scheme for ZNS SSDsYachun Liu, Dan Feng, Jianxi Chen, Jing Hu, Zhouxuan Peng, and Jinlei HuACM Transactions on Architecture and Code Optimization, Sep 2025
@article{Liu_2025, title = {ZNSFQ: An Efficient and High-Performance Fair Queue Scheduling Scheme for ZNS SSDs}, volume = {22}, issn = {1544-3973}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1145/3746230}, doi = {10.1145/3746230}, number = {3}, journal = {ACM Transactions on Architecture and Code Optimization}, publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery (ACM)}, author = {Liu, Yachun and Feng, Dan and Chen, Jianxi and Hu, Jing and Peng, Zhouxuan and Hu, Jinlei}, year = {2025}, month = sep, pages = {1--27}, } - TACDAdaptHM: A Fully Adaptive Data Migration Strategy for Hybrid Memory SystemsZhouxuan Peng, Dan Feng, Jianxi Chen, Jing Hu, Yachun Liu, Jinlei Hu, and 3 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, Mar 2025
@article{Peng_2025, title = {AdaptHM: A Fully Adaptive Data Migration Strategy for Hybrid Memory Systems}, volume = {44}, issn = {1937-4151}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TCAD.2023.3333284}, doi = {10.1109/tcad.2023.3333284}, number = {3}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems}, publisher = {Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)}, author = {Peng, Zhouxuan and Feng, Dan and Chen, Jianxi and Hu, Jing and Liu, Yachun and Hu, Jinlei and Zhang, Jintong and Wan, Tianyu and Chen, Zuoning}, year = {2025}, month = mar, pages = {923--936}, }
2024
- ICCD
 Optimizing Structural Modification Operation for B+-Tree on Byte-Addressable DevicesDingze† Hong, Jinlei† Hu, Jianxi Chen, Dan Feng, and Jian LiuIn 2024 IEEE 42nd International Conference on Computer Design (ICCD), Nov 2024
Optimizing Structural Modification Operation for B+-Tree on Byte-Addressable DevicesDingze† Hong, Jinlei† Hu, Jianxi Chen, Dan Feng, and Jian LiuIn 2024 IEEE 42nd International Conference on Computer Design (ICCD), Nov 2024Persistent Memory (PM) offers both byte-address ability and non-volatility, making it well-suited for accelerating B+-Tree indexes. However, existing persistent B+-Tree indexes face significant performance challenges due to high structural modification operation (SMO) overhead. SMOs often result in costly item migrations and increased tail latency, which severely degrade the overall performance. In this paper, we present SSTree, a high-performance B+– Tree index specifically optimized to address SMO overhead. SSTree introduces three key innovations: (i) efficient leaf node expansion using a list of subnodes to postpone expensive node splits, (ii) delegated fingerprints to speed up search operations across subnodes, and (iii) proactive subnode compaction that employs out-of-place updates to optimize item organization. Our evaluation demonstrates that SSTree delivers up to 4.38× higher write throughput and up to 62× lower tail latency compared to state-of-the-art persistent B+-Tree indexes.
@inproceedings{Hong_2024, title = {Optimizing Structural Modification Operation for B+-Tree on Byte-Addressable Devices}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/iccd63220.2024.00043}, doi = {10.1109/iccd63220.2024.00043}, booktitle = {2024 IEEE 42nd International Conference on Computer Design (ICCD)}, publisher = {IEEE Computer Society}, author = {Hong, Dingze and Hu, Jinlei and Chen, Jianxi and Feng, Dan and Liu, Jian}, year = {2024}, month = nov, pages = {231--238}, }
2023
- ICCD
 RWORT: A Read and Write Optimized Radix Tree for Persistent MemoryJinlei Hu, Wei Zijie, Chen Jianxi, and Dan FengIn 2023 IEEE 41st International Conference on Computer Design (ICCD), Nov 2023
RWORT: A Read and Write Optimized Radix Tree for Persistent MemoryJinlei Hu, Wei Zijie, Chen Jianxi, and Dan FengIn 2023 IEEE 41st International Conference on Computer Design (ICCD), Nov 2023Tree index structures are widely employed in modern storage systems to support high-performance queries. Persistent memory (PM) brings a new opportunity and challenge for tree indexes. Among persistent tree indexes, we find the radix tree is more suitable than B-Tree for the byte-ability of PM. However, the hierarchy of radix remains excessively high, resulting in high read latency. Node splitting imposes a significant overhead on PM. To address these challenges, we propose RWORT, a read and write optimized radix tree for PM. The key focus of RWORT is to minimize random access in PM and provide efficient write operations. RWORT proposed a hierarchical compression mechanism to significantly reduce the tree height. Additionally, RWORT incorporates mini bloom filters to reduce unnecessary access on PM. For efficient write operations, RWORT uses the lazy split flag and the double-linked pointers to reduce the critical path delay. Furthermore, RWORT introduces a low-overhead ring-based bit tree allocator that improves allocation efficiency on PM. Our experiments show that RWORT improves up to 1.62x/4.91x respectively compared to the state-of-the-art radix tree/B-Tree. RWORT also exhibits higher performance in real-world storage systems such as Memcached.
@inproceedings{Hu_2023_RWORT, title = {RWORT: A Read and Write Optimized Radix Tree for Persistent Memory}, url = {https://doi.ieeecomputersociety.org/10.1109/ICCD58817.2023.00038}, doi = {10.1109/ICCD58817.2023.00038}, booktitle = {2023 IEEE 41st International Conference on Computer Design (ICCD)}, author = {Hu, Jinlei and Zijie, Wei and Jianxi, Chen and Feng, Dan}, year = {2023}, keywords = {memory management;vegetation;delays;indexes;resource management;optimization}, pages = {194--197}, publisher = {IEEE Computer Society}, address = {Los Alamitos, CA, USA}, month = nov, }


